OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 71: COST ESTIMATING
This Check Point Is Available By Subscription Only,
But You Can Still Check Out The Menu Below. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 71: COST ESTIMATING
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 71 Below And Click. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
WELCOME TO CHECK POINT 71 |
|
| |
HOW CAN YOU BENEFIT FROM CHECK POINT 71? |
| |
| The main purpose of this check point is to provide you and your management team with detailed information about Cost Estimating and how to apply this information to maximize your company's performance. |
| |
| In this check point you will learn: |
| |
• About the purpose of cost estimating.
• About factors which influence the cost estimating procedure.
• About comparison between costing and pricing hourly rates.
• About six steps in the standard cost estimating procedure.
• About two basic cost accounting methods.
• About applications of the job order costing method.
• About applications of the process costing method.
• How to use a cost estimating worksheet to prepare a cost estimate.
• About make-or-buy decisions related to cost estimating.
• About determining delivery dates for products and services... and much more. |
| |
LEAN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR CHECK POINT 71 |
| |
| You and your management team should become familiar with the basic Lean Management principles, guidelines, and tools provided in this program and apply them appropriately to the content of this check point. |
| |
| You and your team should adhere to basic lean management guidelines on a continuous basis: |
| |
| • |
Treat your customers as the most important part of your business. |
| • |
Provide your customers with the best possible value of products and services. |
| • |
Meet your customers' requirements with a positive energy on a timely basis. |
| • |
Provide your customers with consistent and reliable after-sales service. |
| • |
Treat your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates with genuine respect. |
| • |
Identify your company's operational weaknesses, non-value-added activities, and waste. |
| • |
Implement the process of continuous improvements on organization-wide basis. |
| • |
Eliminate or minimize your company's non-value-added activities and waste. |
| • |
Streamline your company's operational processes and maximize overall flow efficiency. |
| • |
Reduce your company's operational costs in all areas of business activities. |
| • |
Maximize the quality at the source of all operational processes and activities. |
| • |
Ensure regular evaluation of your employees' performance and required level of knowledge.
|
| • |
Implement fair compensation of your employees based on their overall performance.
|
| • |
Motivate your partners and employees to adhere to high ethical standards of behavior. |
| • |
Maximize safety for your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates. |
| • |
Provide opportunities for a continuous professional growth of partners and employees. |
| • |
Pay attention to "how" positive results are achieved and constantly try to improve them. |
| • |
Cultivate long-term relationships with your customers, suppliers, employees, and business associates. |
|
|
|
1. THE PURPOSE OF THE COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
 |
|
THE PURPOSE OF THE COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
Business owners and operations managers must be fully familiar with sound cost estimating procedures which are an essential element of every profitable business.
When inquiries for jobs, products, services, contracts, or projects are received from prospective customers, it is necessary to prepare accurate Cost Estimates and to specify delivery or completion dates.
The Cost Estimating Procedure forms the basis for Quotations on pending orders and assists in determining the Final Selling Price of products and services. This procedure entails preparation of a statement summarizing quantities and costs of required materials, production times, bought-out components, and sub-contracting services.
Furthermore, cost estimating provides a foundation for thorough financial control of operational activities within the organization. Thus, it is important to develop such a procedure for various types of activities and to ensure that all Cost Factors are properly taken into account. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
|
2. FACTORS WHICH INFLUENCE THE COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
 |
|
Some of the major factors influencing the Cost Estimating Procedure are outlined below. |
FACTORS WHICH INFLUENCE THE COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
1. |
Previous cost estimates. |
2. |
Previous actual cost records. |
3. |
Current cost of materials. |
4. |
Current hourly rates. |
5. |
Current cost of sub-contracting services. |
6. |
Estimated usage of materials, labor, equipment and sub-contracting services. |
7. |
Estimated quantities to be manufactured or processed. |
8. |
Current level of productivity and plant capacity utilization. |
9. |
Availability of time for production or operations. |
10. |
Competitive situation in the marketplace. |
11. |
Possibility of repeat orders. |
12. |
Mature judgment and professional expertise. |
|
|
|
3. COMPARISON BETWEEN COSTING AND PRICING HOURLY RATES |
 |
|
COST ESTIMATING INFORMATION |
Although cost estimating represents one of the basic functions within the operations department, its accuracy depends upon the information supplied by the financial department. Cost Estimating Information includes two types of Hourly Rates presented below. |
TWO HOURLY RATES IN COST ESTIMATING |
Hourly Overhead Recovery Rate,
Or Hourly Rate
Used For Costing Purposes. |
Hourly Rate Chargeable To Customers, Or Hourly Rate
Used For Pricing Purposes. |
This rate is the amount you can charge your customers through man-hour, plant-hour, machine-hour, or man-machine-hour, to recover all your company's costs, or overheads, only. |
This rate is the amount you can charge your customers through man-hour, plant-hour, machine-hour, or man-machine-hour, to recover all your company's costs, or overheads, plus the budgeted profit margin contribution. |
Since this rate excludes the budgeted profit margin contribution, you must add your profit to your total cost, to meet or exceed your budgeted profit margin. Hourly recovery rates are discussed in detail in Tutorial 3. |
Since this rate already includes the budgeted profit margin contribution, you don't have to add anything else, unless you want to make more profit. You may also choose to offer a discount, as long as you remember what your real bottom-line cost is. Hourly rates chargeable to customers are discussed in detail in Tutorial 3. |
| |
|
Note:
It is essential that you and your management team do not confuse the hourly rates. This procedure is called "Cost Estimating", although you may use both "Costing" and "Pricing" hourly rates as discussed. Please consult with your accountant or CPA, if required. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
4. THE STANDARD COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
 |
|
BASIS FOR THE STANDARD COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |
The effectiveness of Cost Estimating depends not only upon the estimator, but also upon the overall efficiency of the operations department and the ability of the operations manager to plan, coordinate and control the work in the facility.
Hourly Recovery Rates, or simply Hourly Rates, may be expressed in dollars per labor-hour or dollars per machine-hour and provide the basis for a standard cost estimating procedure.
The Standard Cost Estimating Procedure comprises a number of steps and is summarized below. |
STEPS IN THE STANDARD COST ESTIMATING PROCEDURE |

Step 1: Examine details of work to be estimated, such as job, product, service, project, or contract specifications, drawings, materials, quantities, and delivery date.

Step 2: Break down the job, product, service, project, or contract into individual components, parts, and operations and summarize them in a Costing Sheet.

Step 3: Decide whether to make, buy, or sub-contract the individual component, part, or operation. |
 |
|
 |
Step 4a: If the component, part, or operation is to be produced, specify all activities and estimate the cost of drawings, tooling, raw materials, operational capacity, and labor requirements. |
|
Step 4b: If the component, part, or operation is to be purchased or sub-contracted, obtain relevant final prices and delivery dates from prospective suppliers or sub-contractors. |
 |
|
 |
|
|
Step 5: Determine when drawings, tooling, raw materials, equipment capacity, labor, bought-out or sub-contracted components, parts, or operations are available.

Step 6: Develop an appropriate cost and delivery schedule for the completed job, finished product, service, project, or contract. |
|
|
5. TWO BASIC COST ACCOUNTING METHODS |
 |
|
COST ACCOUNTING METHODS |
Standard Cost Estimating Procedures are constantly used for various operational activities in manufacturing and non-manufacturing companies alike. These procedures have been developed in accordance with two basic Cost Accounting Methods which are generally used by cost accountants and cost estimators. Both methods are discussed in detail in Tutorial 3 and summarized below. |
TWO BASIC COST ACCOUNTING METHODS |
 |
|
 |
Job Order Costing |
|
Process Costing |
| Products and services are produced or supplied to special orders or in batches. |
|
Products and services are produced on a continuous "flow" basis. |
 |
|
 |
Service Company |
|
Service Company |
| Custom service is rendered to a special customer order on a non-repetitive basis. |
|
Standard service is rendered to several customers on a continuous "flow" basis. |
 |
|
 |
Merchandising Company |
|
Merchandising Company |
| Products are supplied on a wholesale or retail basis. |
|
Not applicable. |
 |
|
 |
Manufacturing Company |
|
Manufacturing Company |
| Products are manufactured in a job shop or batch production environments. |
|
Products are manufactured in a flow production environment. |
|
|
|
|
6. THE JOB ORDER COSTING METHOD |
 |
|
THE JOB ORDER COSTING METHOD |
The Job Order Costing Method entails costing of raw materials, labor, use of operational capacity, and sub-contracting services for each job, product, service, project, or contract on an individual basis. This method is commonly used for estimation of costs in several types of environments illustrated below. |
APPLICATION OF THE JOB ORDER COSTING METHOD |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Job Shop Production |
Batch
Production |
Custom
Services |
Special
Projects |
Contracts |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
Please watch these excellent videos professionally narrated and produced by Susan Crosson and SFCC: |
|
© 2008 - 2013 Susan Crosson and CFCC. All rights reserved. |
|
|
7. THE PROCESS COSTING METHOD |
 |
|
THE PROCESS COSTING METHOD |
The Process Costing Method entails costing of raw materials, labor, use of operational capacity, and sub-contracting services for a particular manufacturing or service process and allocating the overall cost to the total number of product or service units produced. This method is commonly used for estimation of costs in several types of environments illustrated below. |
APPLICATION OF THE PROCESS COSTING METHOD |
 |
|
 |
Flow Production
Environment |
|
Standard
Services |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
Please watch these excellent videos professionally narrated and produced by Susan Crosson and SFCC: |
|
© 2008 - 2013 Susan Crosson and CFCC. All rights reserved. |
|
|
8. COST ESTIMATE WORKSHEET |
 |
|
COST ESTIMATE WORKSHEET |
Irrespective of the costing method used, the standard cost estimating procedure necessitates a thorough understanding of all material, labor, operational capacity, and sub-contracting service requirements. These requirements should be identified and summarized in a Cost Estimate Worksheet. A typical illustration of a Cost Estimate Worksheet is presented below.
Since the product manufacturing or service operational processes pass through various work centers, the labor and operational capacity input per work center needs to be estimated on a time basis and corresponding hourly rates need to be applied. |
|
|
9. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
COST ESTIMATE WORKSHEET |
 |
|
COST ESTIMATE WORKSHEET |
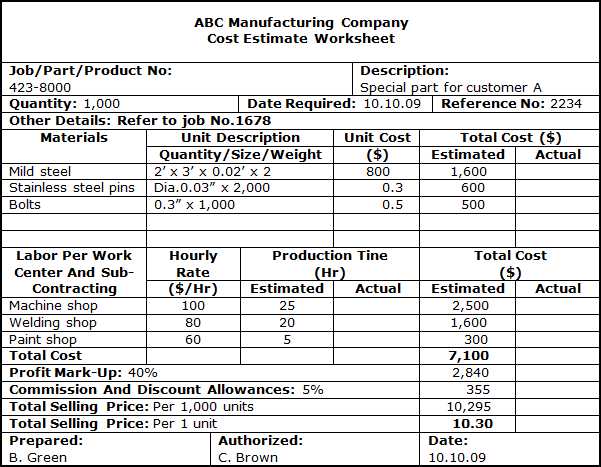
|
|
|
10. MAKE-OR-BUY DECISIONS |
 |
|
MAKE-OR-BUY DECISIONS |
It is often necessary to decide whether to manufacture a particular component or to purchase it from another supplier. In fact, most Make-Or-Buy Decisions for operational activities are made during the cost estimating procedure.
A Company's Buyer must obtain appropriate prices for materials and services and pass the information to the cost estimator, who is ultimately responsible for make-or-buy decisions. Subsequently, all Buy-Out Costs should be identified in advance and specified in the final Cost Estimate Worksheet.
Prior to the commencement of any operational activity, it is essential to identify whether operational capacity is available, and if not, to pre-select a suitable sub-contractor. All Sub-Contracting Service Costs should be identified in advance and specified in the final Cost Estimate Worksheet. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
Please watch these excellent videos professionally narrated and produced by Susan Crosson and SFCC: |
|
© 2008 - 2013 Susan Crosson and CFCC. All rights reserved. |
|
|
11. COST ESTIMATING SOFTWARE PROGRAMS |
 |
|
OPTIONAL COST ESTIMATING METHODS |
|
Cost estimating tasks can be completed manually by using pre-determined Hourly Overhead Recovery Rates which take into account all relevant costs incurred in a particular operational process. Cost estimating tasks can be also accomplished by using various software programs developed for cost estimating purposes. |
|
There are several cost estimating software programs specifically developed for various industries. Some of the most popular estimating programs for construction industry, for example, are presented below: |
|
|
You may find additional cost estimating software programs at TopTenReviews and other similar sites online. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
12. DETERMINATION OF DELIVERY DATES |
 |
|
DETERMINATION OF DELIVERY DATES |
Cost estimating procedure also entails determination of product or service Delivery Dates. This, in turn, is a part of the Production Scheduling Process which is discussed in detail in Tutorial 4. Hence, the cost estimator should determine the total working time and identify the existing availability of Operational Capacity and Labor Resources.
Each operation should be fitted into the existing Production Schedule or Operations Schedule in accordance with available operational capacity, that is, total capacity less the existing workload in the operations department. If the existing workload does not permit timely completion of a particular assignment, the Cost Estimator should consider whether to use overtime operational capacity or to quote a late delivery to a customer. |
|
|
13. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
14. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
Cost Estimating Is The Art Of Satisfying
A Customer And Making A Profit At The Same Time!
|
Go To The Next Open Check Point In This Promotion Program Online. |
| |
|




