|
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 44: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 44 Below And Click. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
|
1. THREE IMPORTANT FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
 |
|
INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
Business owners and financial managers must be able to properly “read” and interpret all financial statements, which are of prime importance to every business organization.
Accurate and comprehensive maintenance of the bookkeeping system facilitates timely preparation of Financial Statements. These statements consist of three important documents, illustrated below, which are designed to provide the most updated information regarding three essential parameters of the company's financial status:
| • |
Solvency |
| • |
Profitability |
| • |
Liquidity |
|
THREE IMPORTANT FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Balance
Sheet |
|
Income
Statement |
|
Statement
Of Cash Flows |
| A balance sheet provides information about a company's solvency, i.e. the excess of its assets over its liabilities at a specific moment of time. |
|
Income statement provides information about a company's profitability, i.e. the excess of its revenues over its expenses during a specific period. |
|
A statement of cash flows provides information about a company's liquidity, i.e. the excess of its available and incoming funds over its outgoing funds during a specific period. |
|
| |
| |
| Financial statements can be prepared manually or by using a specific Accounting Software Program as discussed in detail in Tutorial 3. |
| |
| THREE MOST POPULAR ACCOUNTING SOFTWARE PROGRAMS |
| |
| There are several excellent accounting software programs available to small business owners at present. According to TopTenReviews.com, three most popular accounting software packages are: |
| |
|
1. Sage 50 Complete Accounting 2013.
2. QuickBooks Pro 2011.
3. Bookkeeper 2012. |
|
|
|
2. BALANCE SHEET |
 |
|
BALANCE SHEET |
A Balance Sheet is a statement of the company's financial position at a specific moment in time.
A balance sheet is referred to as a "snapshot" of the organization's resources and obligations and is intended to describe the financial condition of the company on the date of closing books of account.
The resources, or Assets, available to management are classified into four categories. The obligations, or claims, against these assets are made by creditors and shareholders and are classified as the company's Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity.
A balance sheet merely summarizes the financial position and provides details of all assets and liabilities of the organization at a given date. It does not indicate whether the company makes profit or incurs losses.
The structure of a balance sheet does not depend upon the type of operations, i.e. service, merchandising, or manufacturing companies may have similarly structured balance sheet statements.
A simplified illustration of a typical balance sheet is presented below.
|
CLASSIFICATION OF ASSETS |
No. |
Details |
1. |
Current Assets.
Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory (merchandise, direct materials, work-in-process, and finished goods), receivables, prepaid expenses, refundable deposits, and short-term investments. |
2. |
Capital Assets.
Capital assets, also known as Fixed Assets or Long-Term Assets, include land, buildings, equipment, furniture, and vehicles purchased for use. |
3. |
Long-Term Investments.
Long-term investments include land, buildings, or equipment purchased for speculative reasons. |
4. |
Intangible Assets.
Intangible assets include patents, copyrights, trademarks, and goodwill. |
|
| |
CLASSIFICATION OF LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY |
No. |
Details |
1. |
Current Liabilities.
Current liabilities include accounts payable, bank overdraft (used-up credit line), current portion of a long-term debt, dividends payable, notes payable, payroll liability, taxes payable, product warranty liability, and other accrued liabilities. |
2. |
Long-Term Liabilities.
Long-term liabilities include bonds payable, capital leases, mortgages payable, and pension liability. |
3. |
Shareholders' Equity.
Shareholders' equity includes the value of the issued stock and retained earnings. |
|
|
|
|
3. ACCOUNTING PERIOD |
 |
|
ACCOUNTING PERIOD |
While a Balance Sheet is prepared to reflect a company’s financial condition on a particular date, an Income Statement and a Statement Of Cash Flows are prepared to cover a particular period of the company's operating activities. This period is termed the Accounting Period and represents an important milestone in the company's life.
The length of the accounting period is commonly accepted as one full year, known as the Fiscal Year or Financial Year.
Management has the option of selecting the beginning of the company's fiscal year in accordance with the particular operating conditions and other relevant factors.
Sometimes, financial statements may be drawn up on semi-annually, quarterly or monthly basis, depending upon the specific requirements of the shareholders, management and outside creditors. |
|
|
|
4. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
BALANCE SHEET |
 |
|
|
BALANCE SHEET |
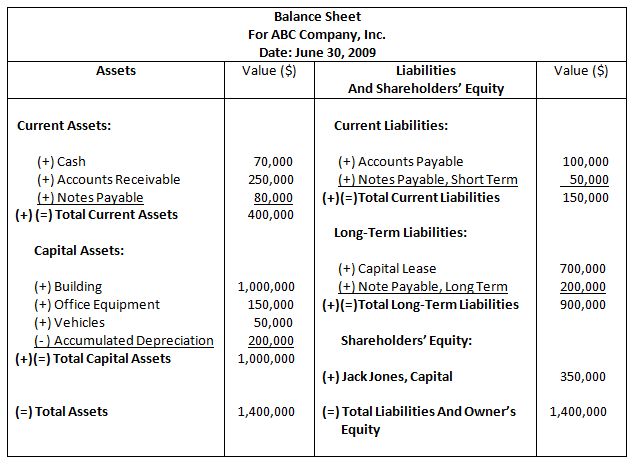 |
|
|
|
5. INCOME STATEMENT |
 |
|
INCOME STATEMENT
An Income Statement summarizes the amounts of operating revenues earned and operating expenses incurred during a specific accounting period.
Income statements, also known as the Profit And Loss Account or P & L Account, should be prepared on a monthly basis to provide management with an essential financial tool designed to measure and control the company’s operational performance. The statement summarizing twelve months of the company's operational performance is termed the Annual Income Statement, or simply the Income Statement, and it represents the second important financial statement.
The prime result of an income statement is the determination of Gross Margin From Sales (for merchandising and manufacturing companies) and Net Income for all types of companies, i.e. Net Profit (before and after taxes).
The final presentation form of revenues, expenses, and net income depends upon the nature of the company's operating activities. This is reflected in three different forms of income statement illustrated below.
THREE FORMS OF AN INCOME STATEMENT |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Income Statement
For
A Service
Company |
|
Income Statement
For
A Merchandising
Company |
|
Statement
Of Cost
Of Goods
Manufactured |
| |
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
Income Statement
For
A Manufacturing
Company |
|
| |
| |
OPERATING REVENUES AND EXPENSES |
Operating Revenues include all amounts earned by the company as a result of rendering services or selling goods to customers during a specified accounting period, while Operating Expenses include all costs incurred by the company during the same period. Operating expenses for manufacturing companies are also known as Manufacturing Costs, or Factory Overhead, or Factory Burden.
Simplified examples of typical income statements for a service, merchandising and manufacturing companies are presented below. |
|
|
6. CLASSIFICATION OF INVENTORY FOR ACCOUNTING PURPOSES |
 |
|
INVENTORY VALUES
Service Companies generally don’t have to carry special types of inventory, except for consumable products and some spare parts, to conduct their business operations. For this reason, the income statement for a service company doesn’t take into account the fluctuation of inventory during a specific fiscal period. An exception would be a service business, like a car repair shop, which may have to carry various types of spare parts in large quantities. In this case the fluctuation in inventory must be accounted for to ensure accurate determination of profit and loss during a specific period.
On the other hand, Merchandising Companies, i.e. Wholesalers and Retailers, and Manufacturing Companies must carry substantial amounts of inventory to enable them to conduct their business activities. For this reason, the income statements for merchandising and manufacturing companies must contain detailed information pertaining to the Value Of Inventory carried by the organization during a particular accounting period.
The Classification Of Inventory also depends upon the nature of the company's activities illustrated below.
CLASSIFICATION OF INVENTORY |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Service
Company |
|
Merchandising
Company |
|
Manufacturing
Company |
|
A service company usually does not carry inventory except for certain consumable items, e.g. supplies, or spare parts.
| • |
Spare Parts |
| • |
Consumable Supplies |
|
|
A merchandising company carries inventory for resale known as Merchandise Inventory. |
|
A manufacturing company carries three types of inventory:
| • |
Direct Materials Inventory |
| • |
Work-In-Process Inventory |
| • |
Finished Goods Inventory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A SERVICE COMPANY |
 |
|
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A SERVICE COMPANY |
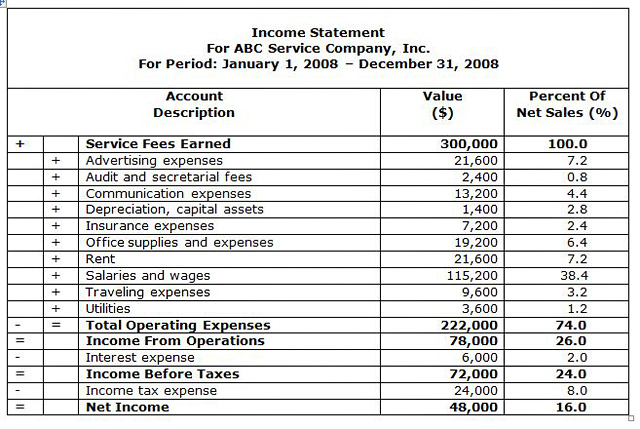 |
|
|
8. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A MERCHANDISING COMPANY |
 |
|
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A MERCHANDISING COMPANY |
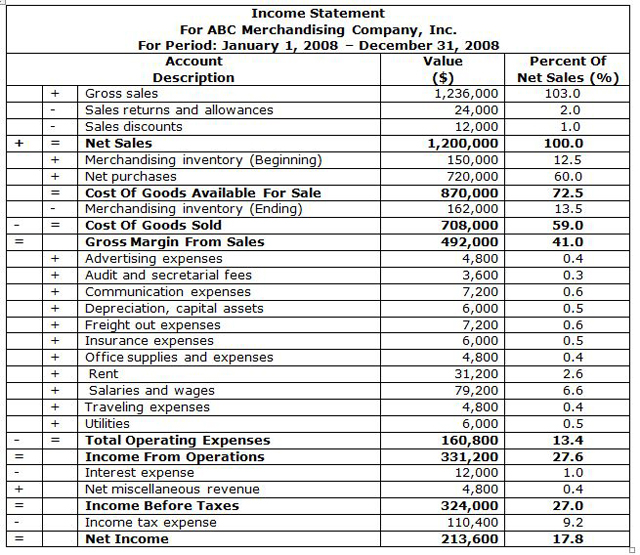 |
|
|
|
9. STATEMENT OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED |
 |
|
STATEMENT OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED |
Additional information pertinent only to manufacturing companies is included in the Statement Of Cost Of Goods Manufactured, also known as Cost Of Goods Statement, or COGS.
The main purpose of this statement is to summarize all manufacturing costs incurred during a specific accounting period and to establish the cost of goods manufactured. This cost will be subsequently transferred into the income statement to determine the net income for a manufacturing company during a specified accounting period. |
|
|
|
10. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
STATEMENT OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED |
 |
|
STATEMENT OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED |
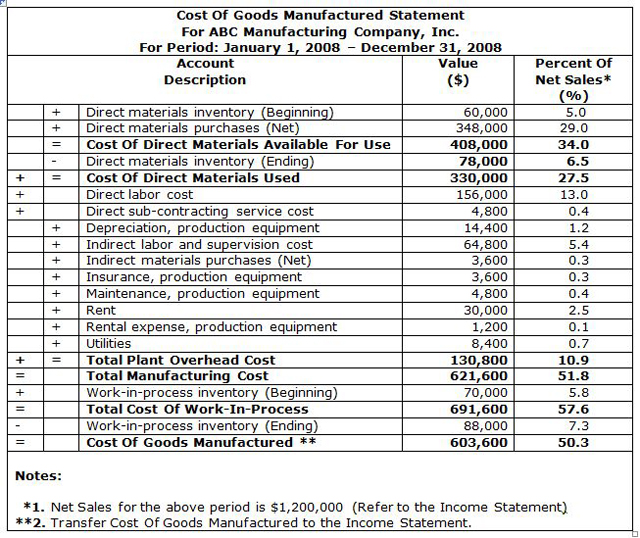 |
|
|
11. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A MANUFACTURING COMPANY |
 |
|
INCOME STATEMENT FOR A MANUFACTURING COMPANY |
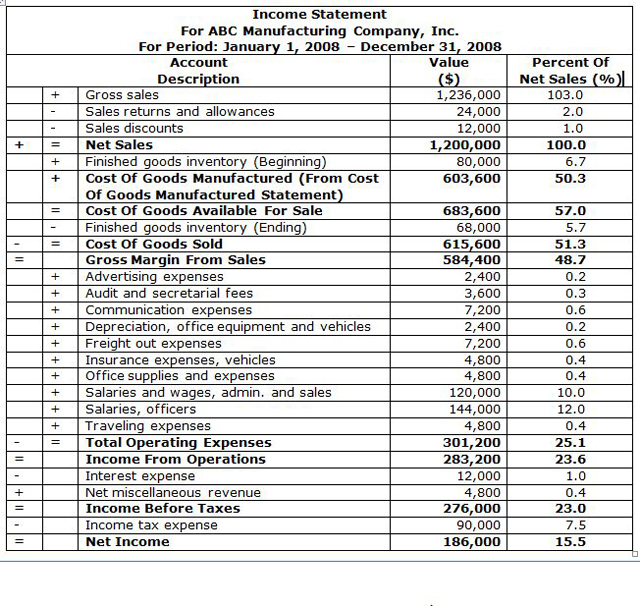 |
|
|
12. STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS |
 |
|
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS |
A Statement Of Cash Flows is the third important financial statement, which summarizes all receipts and payments of funds by an organization during a specified accounting period.
The statement of cash flows reflects the movement of funds as a result of all operating, investing, and financing activities of the organization. The structure of a statement of cash flows does not depend upon the type of operations, i.e. service, merchandising, or manufacturing company may have a similarly structured statement of cash flows.
A simplified example of statement of cash flows is presented below. |
|
|
|
13. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS |
 |
|
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS |
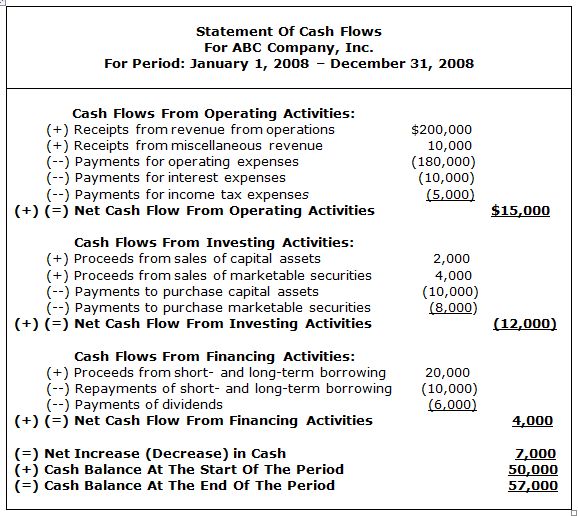 |
|
|
14. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
15. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
Whatever You Do Today Will Definitely Show Up Tomorrow! |
| |
|



