GENERAL MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 14: ORGANIZATIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION
This Check Point Is Available By Subscription Only,
But You Can Still Check Out The Menu Below. |
|
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 14: ORGANIZATIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 14 Below And Click. |
|
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
WELCOME TO CHECK POINT 14 |
|
| |
HOW CAN YOU BENEFIT FROM CHECK POINT 14? |
| |
| The main purpose of this check point is to provide you and your management team with detailed information about Organizational Departmentalization and how to apply this information to maximize your company's performance. |
| |
| In this check point you will learn: |
| |
• What is the organizational departmentalization?
• About departmentalization by function.
• About the advantages of functional departmentalization.
• About a divisional structure.
• About departmentalization by product.
• About departmentalization by service.
• About departmentalization by market.
• About departmentalization by customer.
• About departmentalization by territory.
• About matrix structure... and much more. |
| |
LEAN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR CHECK POINT 14 |
| |
| You and your management team should become familiar with the basic Lean Management principles, guidelines, and tools provided in this program and apply them appropriately to the content of this check point. |
| |
| You and your team should adhere to basic lean management guidelines on a continuous basis: |
| |
| • |
Treat your customers as the most important part of your business. |
| • |
Provide your customers with the best possible value of products and services. |
| • |
Meet your customers' requirements with a positive energy on a timely basis. |
| • |
Provide your customers with consistent and reliable after-sales service. |
| • |
Treat your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates with genuine respect. |
| • |
Identify your company's operational weaknesses, non-value-added activities, and waste. |
| •. |
Implement the process of continuous improvements on organization-wide basis. |
| • |
Eliminate or minimize your company's non-value-added activities and waste. |
| • |
Streamline your company's operational processes and maximize overall flow efficiency. |
| • |
Reduce your company's operational costs in all areas of business activities. |
| • |
Maximize the quality at the source of all operational processes and activities. |
| • |
Ensure regular evaluation of your employees' performance and required level of knowledge.
|
| • |
Implement fair compensation of your employees based on their overall performance.
|
| • |
Motivate your partners and employees to adhere to high ethical standards of behavior. |
| • |
Maximize safety for your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates. |
| • |
Provide opportunities for a continuous professional growth of partners and employees. |
| • |
Pay attention to "how" positive results are achieved and constantly try to improve them. |
| • |
Cultivate long-term relationships with your customers, suppliers, employees, and business associates. |
|
|
|
1. WHAT IS ORGANIZATIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION? |
 |
|
THE ORGANIZING PROCESS |
|
One of the main tasks of every business owner and manager in the organizing process is the sub-division of the company into a number of specialized working groups to ensure maximum performance.
This task is known as Organizational Departmentalization. The prime purpose of organizational departmentalization is to group people and activities into departments to allow orderly functioning of the enterprise.
The complexity of Departmentalization Methods depends upon the nature, size, and objectives of a particular organization. Some commonly used departmentalization methods are illustrated below. |
DEPARTMENTALIZATION METHODS |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Departmentalization
By
Function |
Departmentalization
By
Product Or Service |
Departmentalization
By
Market Or Customer |
Departmentalization
By
Territory |
|
|
| |
| ARE YOU A ONE-PERSON BUSINESS OWNER? |
| |
If you are a one-person business owner, you may skip this check point at this stage because it is not applicable to a micro-business like yours.
However, it will be very beneficial for you to become familiar with the content of the entire check point in the future, because one day you may decide to take your business to the next level and employ additional employees within your organization. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
2. DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY FUNCTION |
 |
|
WHAT IS DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY FUNCTION? |
Departmentalization By Function, or Functional Departmentalization, is commonly used by small and medium-sized companies that offer a limited range of product or services to customers.
Departmentalization by function facilitates the development of a Functional Structure and provides a basis for separating various functions within the organization. Such functions include general administration, human resources, finance and accounting, operations, marketing and sales as illustrated below. |
ILLUSTRATION OF A FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE |

General Administration Department
President/Chief Executive Officer (CEO):
Planning, Organizing, Leading, And Controlling All Operational Management Activities. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Human
Resources
Department |
Financial
Department |
Operations
Department |
Marketing
And Sales
Department |
Vice President,
Human Resources: |
Vice President,
Finance/CFO: |
Vice President,
Operations/COO: |
Vice President,
Marketing And Sales: |
- Job descriptions.
- Job specifications.
- Employee: planning,
recruitment,
orientation,
training,
development,
compensation
planning,
career
management,
performance
appraisal,
motivation.
- Labor-
management
relations.
- Conflict
management.
- Safety and health.
|
- General accounting.
- Bookkeeping.
- Financial
analysis.
- Budgeting:
operating,
cash, and
capital
expenditure.
- Tax
strategies.
- Sources of finance.
- Control of: cash, credit,
expenditure,
inventory, and capital assets.
- Costing and pricing of products and services.
- Management
accounting reports.
- Data processing.
- Management
of financial
department
employees.
|
- Facility
design and organization.
- Product, service, and process design.
- Design
office.
- Equipment evaluation,
selection,
maintenance,
and
replacement.
- Plant layout.
- Tool control.
- Cost estimating.
- Operation
planning and control.
- Quality
control.
- Material
purchasing,
control,
storage,
and
dispatch.
- Labor
management.
|
- Market research,
segmentation,
measurement,
and
forecasting.
- Marketing
strategy
(product,
price,
promotion,
and
distribution).
- Marketing
planning
and
budgeting.
- Sales
planning
and
budgeting.
- Sales force
recruitment,
training,
compensation,
performance
appraisal,
management,
and control.
|
|
|
|
|
3. ADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION |
 |
|
ADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION |
The example of Functional Departmentalization, illustrated above, presents a typical design for a small or medium-sized manufacturing company.
Functional departmentalization in a non-manufacturing organization can be carried out in a similar manner, although the operations management function may include additional functional responsibilities, depending upon the specific nature of operations, namely: service, merchandizing (wholesale or retail), project or contract management.
Every executive manager within a Functional Organization is in charge of a specific range of operational activities on a company-wide basis as outlined below. |
WHO IS IN CHARGE IN A FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION? |
1. |
President, or Chief Executive Officer (CEO), is in charge of all general administration and management activities. |
2. |
Vice President, Human Resources is in charge of all human resources management activities. In many smaller organizations, however, this function is carried out by the President or CEO. |
3. |
Vice President, Finance, or Chief Financial Officer (CFO), is in charge of all financial management activities. |
4. |
Vice President, Operations, or Chief Operations Officer (COO), is in charge of all operations management activities in a manufacturing or non-manufacturing company alike. In many larger manufacturing organizations, this function may be divided into engineering management (design work) and manufacturing management activities. |
5. |
Vice President, Marketing And Sales, is in charge of all marketing and sales activities. In larger organizations this function is divided into two separate functions: Vice President, Marketing and Vice President, Sales. |
|
| |
The main advantages of the Functional Departmentalization Method are summarized below. |
| |
ADVANTAGES OF THE FUNCTIONAL DEPARTMENTALIZATION METHOD |
1. |
It provides a logical, effective, and time-proven method of planning and controlling the performance of each functional activity. |
2. |
It ensures the most efficient utilization of employees following the Principle Of Occupational Specialization within the organization. |
3. |
It simplifies the process of recruiting, training, and managing employees in each department. |
4. |
It facilitates a centralized decision-making process. |
5. |
It enables the executive management team to maintain tight control at the top. |
|
|
|
4. DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE |
 |
|
WHAT IS DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE? |
A Divisional Structure represents a method of departmentalization frequently used by medium-sized and larger organizations in the marketplace.
As an organization grows, it develops new product or service lines, increases the number of customers, and expands into new territories. As a result, a simple functional structure may become less effective, thus creating apparent problems in planning and managing operational activities.
This represents a prime disadvantage for Growing Organizations that operate in a rapidly changing consumer and technological environment and that offer a broad range of products or services to a large number of customers. For this reason a divisional structure may prove to be more effective. There are several types of divisional structures illustrated below. |
THREE TYPES OF DIVISIONAL STRUCTURES |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Departmentalization
By
Product Or Service |
|
Departmentalization
By
Market Or Customer |
|
Departmentalization
By
Territory |
|
|
| |
All three types of Divisional Structures are explained in detail next. Irrespective of the type of departmentalization, however, all companies with a divisional structure have similar characteristics outlined below. |
| |
CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPANY WITH A DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE |
1. |
Divisional managers are in charge of all operational activities within their divisions, such as general administration, human resources, finance and accounting, operations, marketing and sales. |
2. |
Divisional managers are personally accountable to the company's president for the profitability of their divisions. |
3. |
Functional vice presidents supervise and coordinate all operational activities within their areas of responsibility and provide support to divisional managers. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
5. DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE |
 |
|
WHAT IS DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE? |
Departmentalization By Product Or Service is particularly useful for organizations which handle diversified types of products or services.
Many medium-sized and larger multi-product and multi-service companies are departmentalized according to a product or service organizational structure. In a company departmentalized by product or service, all product or service lines are grouped into separate divisions as illustrated below. |
ILLUSTRATION OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE |
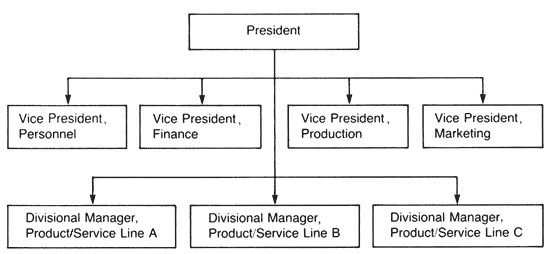 |
|
|
6. ADVANTAGES OF THE DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE |
 |
|
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE |
| Departmentalization By Product Or Service has several advantages and disadvantages outlined below. |
| |
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY PRODUCT OR SERVICE
| Advantages: |
|
Disadvantages: |
- Tasks can be accomplished in a more efficient manner since all activities, skills, and resources required for a line of product or services are grouped within one division under one person.
- Divisional managers have more authority which enhances the quality and speed of their decisions.
- The overall performance of each division can be effectively measured in terms of its profit or loss.
|
|
- This type of structure requires more persons with general management skills.
- Some of the operating functions may also be duplicated in various divisions, thus creating the need for additional number of employees and higher overhead costs.
- The decentralization of the decision making may create conflicts between certain tasks and priorities within the organization.
|
|
|
|
|
7. DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER |
 |
|
WHAT IS DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER? |
Departmentalization By Market Or Customer is particularly useful for medium-sized and larger companies that operate in diversified markets and deal with a substantial number of customers.
A large manufacturing company, for example, might have separate divisions for different types of markets (e.g. industrial or consumer), or for customers in different industries (e.g. chemical or engineering) as illustrated next. |
ILLUSTRATION OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER |
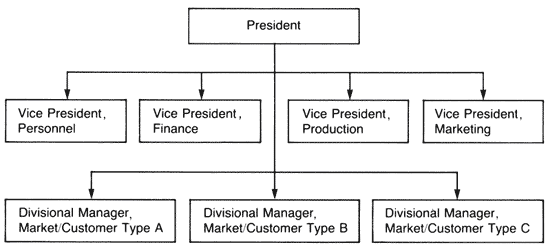 |
|
|
8. ADVANTAGES OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER |
 |
|
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER |
| Departmentalization By Market Or Customer also has several advantages and disadvantages outlined below. |
| |
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY MARKET OR CUSTOMER
| Advantages: |
|
Disadvantages: |
- This type of structure enables the organization to serve diversified markets or types in the most efficient manner.
- Divisional managers carry full authority and responsibility within their divisions and are accountable to the president for their performance.
- Each functional vice president is responsible for supervision and coordination of all operational activities within a defined area and provision of support to divisional managers.
|
|
- This type of structure requires more persons with general management skills.
- Some of the operating functions may also be duplicated in various divisions, thus creating the need for additional number of employees and higher overhead costs.
- The decentralization of the decision making may create conflicts between certain tasks and priorities within the organization.
|
|
|
|
|
9. DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY |
 |
|
WHAT IS DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY |
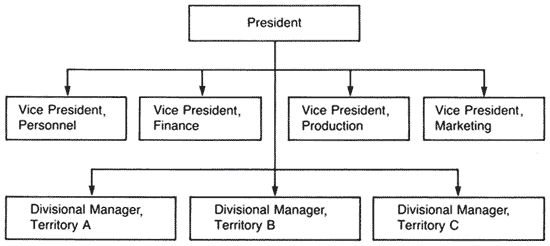
Departmentalization By Territory is particularly useful for medium-sized and larger companies that conduct their business in different geographic regions.
A large manufacturing company, for example, might have separate divisions in East Coast and West Coast regions, or in different countries. Typical departmentalization by territory is illustrated below. |
ILLUSTRATION OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY |
 |
|
|
10. ADVANTAGES OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY |
 |
|
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY |
| Departmentalization By Territory also has several advantages and disadvantages outlined below. |
| |
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF
DEPARTMENTALIZATION BY TERRITORY
| Advantages: |
|
Disadvantages: |
- This type of structure enables the organization to serve local markets in a more efficient manner.
- Divisional managers carry full authority and responsibility within their divisions and are accountable to the president for their performance.
- Each functional vice president is responsible for supervision and coordination of all operational activities within a defined area and provision of support to divisional managers.
|
|
- This type of structure requires more persons with general management skills.
- Some of the operating functions may also be duplicated in various divisions, thus creating the need for additional number of employees and higher overhead costs.
- The decentralization of the decision making may create conflicts between certain tasks and priorities within the organization.
|
|
|
|
|
11. MATRIX STRUCTURE |
 |
|
TWO BASIC TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES |
The departmentalization methods, described earlier, enable management to develop two basic types of organizational structures: a Functional Structure and a Divisional Structure as summarized below. |
TWO PRIME METHODS OF DEPARTMENTALIZATION |
 |
 |
Functional Structure |
Divisional Structure |
| A functional structure facilitates effective specialization and control of operational activities and is particularly suitable for most small and some medium-sized companies. |
A divisional structure provides effective specialization by product or service, market or customer, and territory, and is more suitable for some medium-sized and many larger organizations. |
|
|
| |
WHAT IS A MATRIX STRUCTURE? |
There is, however, a third type of organizational structure which combines the advantages of both functional and divisional structures. This structure, illustrated below, known as a Matrix Structure, is frequently applied to specialized product or project organizations. |
ILLUSTRATION OF A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
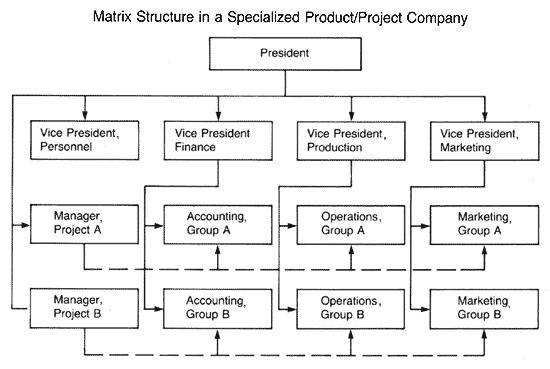 |
|
|
12. ADVANTAGES AND APPLICATIONS OF A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
 |
|
ADVANTAGES AND APPLICATIONS OF A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
In a Matrix Structure the team members in every group have two superiors: the functional vice president and the product or project manager. This creates a Dual Chain Of Command, contradicting the classical Unity Of Command Principle within the organization.
Thus, for example, each member in the Accounting Group A is simultaneously accountable to vice president, finance and to the manager of Project A.
Each executive manager within a matrix organization is in charge of specific functional activities on a company-wide basis. This is similar to the arrangement which exists in a functional organization.
The functional responsibilities of executive managers in a Matrix Organization, based on the previous example, are outlined below. |
EXAMPLES OF FUNCTIONAL RESPONSIBILITIES
OF EXECUTIVE MANAGERS IN A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
1. |
President is in charge of all general management activities. |
2. |
Vice president, human resources, is in charge of all human resources management activities. |
3. |
Vice president, finance, is in charge of all financial management activities, carried out by Accounting Groups A and B. |
4. |
Vice president, operations, is in charge of all operations management activities carried out by operations Groups A and B. |
5. |
Vice president, marketing, is in charge of all marketing and sales management
activities carried out by Marketing Groups A and B. |
|
| |
EXAMPLES OF MANAGEMENT AUTHORITY IN A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
Executive Managers have authority over employees within their department with respect to coordination of functional activities, promotions, and salary recommendations. Project Managers, on the other hand, have authority over respective members of their teams relative to the project execution.
The responsibilities of managers in a Matrix Structure are further clarified below. |
EXAMPLES OF MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITIES IN A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
1. |
Manager, Project A, is in charge of all operational activities carried out by Group A, including accounting, operations, marketing and sales. |
2. |
Manager, Project B, is in charge of all operational activities carried out by Group B, including accounting, operations, marketing and sales. |
3. |
Manager, Project C, is in charge of all operational activities carried out by Group C, including accounting, operations, marketing and sales. |
|
| |
EXAMPLES OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTABILITY IN A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
Project Managers are accountable to the company's president for the profitability of their projects. This is similar to the relationship which exists between the divisional manager and the president in a divisional structure. |
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF A MATRIX STRUCTURE |
A Matrix Structure is particularly useful for companies engaged in various types of projects. This structure provides the organization with the advantages of both functional and divisional methods of departmentalization. One of the prime disadvantages of this structure, however, is frequent confusion among employees as a result of receiving instructions from two superiors.
In order to ensure effective performance of a Matrix Organization, it is essential to coordinate all efforts between functional and divisional managers on a continuous basis. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
13. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
14. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
| |
|
LESSON FOR TODAY:
If You Want To Be A Big Company Tomorrow,
You Have To Start Acting Like One Today!
Thomas J. Watson, CEO, IBM |
Go To The Next Open Check Point In This Promotion Program Online. |
| |
|








