OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 73: MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING
This Check Point Is Available By Subscription Only,
But You Can Still Check Out The Menu Below. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 73: MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 73 Below And Click. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
WELCOME TO CHECK POINT 73 |
|
| |
HOW CAN YOU BENEFIT FROM CHECK POINT 73? |
| |
| The main purpose of this check point is to provide you and your management team with detailed information about Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and how to apply this information to maximize your company's performance. |
| |
| In this check point you will learn: |
| |
• About three main functions and advantages of the MRP system.
• About three sources of information for the MRP system.
• About a master production schedule and the inner workings of the MRP system.
• About a bill of materials and a product structure tree.
• About inventory status files and inventory records.
• What can the MRP system do for your company?
• About time scaled assembly charts.
• About primary and secondary reports.
• About manufacturing resources planning system (MRPII).
• About enterprise resource planning system (ERP)... and much more. |
| |
LEAN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR CHECK POINT 73 |
| |
| You and your management team should become familiar with the basic Lean Management principles, guidelines, and tools provided in this program and apply them appropriately to the content of this check point. |
| |
| You and your team should adhere to basic lean management guidelines on a continuous basis: |
| |
| • |
Treat your customers as the most important part of your business. |
| • |
Provide your customers with the best possible value of products and services. |
| • |
Meet your customers' requirements with a positive energy on a timely basis. |
| • |
Provide your customers with consistent and reliable after-sales service. |
| • |
Treat your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates with genuine respect. |
| • |
Identify your company's operational weaknesses, non-value-added activities, and waste. |
| • |
Implement the process of continuous improvements on organization-wide basis. |
| • |
Eliminate or minimize your company's non-value-added activities and waste. |
| • |
Streamline your company's operational processes and maximize overall flow efficiency. |
| • |
Reduce your company's operational costs in all areas of business activities. |
| • |
Maximize the quality at the source of all operational processes and activities. |
| • |
Ensure regular evaluation of your employees' performance and required level of knowledge.
|
| • |
Implement fair compensation of your employees based on their overall performance.
|
| • |
Motivate your partners and employees to adhere to high ethical standards of behavior. |
| • |
Maximize safety for your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates. |
| • |
Provide opportunities for a continuous professional growth of partners and employees. |
| • |
Pay attention to "how" positive results are achieved and constantly try to improve them. |
| • |
Cultivate long-term relationships with your customers, suppliers, employees, and business associates. |
|
|
|
1. WHAT IS THE MRP SYSTEM? |
 |
|
THE MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING SYSTEM |
Business owners and operations managers must be fully familiar with the material requirements planning procedures which represent an essential function in every manufacturing and some non-manufacturing organizations.
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a computerized system which aims to calculate the quantity and determine the timing of materials, parts, and components required to complete a finished product.
MRP is considered one of the most important operations and inventory management systems used by many manufacturing organizations of various sizes. This system is designed to enable manufacturing companies to become more cost-effective in a highly competitive global market environment.
The popularity of MRP systems has grown considerably over the last several decades through contributions by several experts, including:
• Joseph Orlicky
• George W. Plossl
• Oliver Wight
In addition, the Association For Operations Management, formerly known as the American Production And Inventory Control Society (APICS), plays a crucial role in promoting knowledge in the areas of material requirements planning, operational planning and control, inventory management, and supply chain management. APICS also offers special certification programs in various areas of operations and inventory control, including MRP systems.
Additional information about the Association For Operations Management is available online. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
2. THREE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
THE MRP SYSTEM |
The three main functions of the MRP System have been summarized by Joseph Orlicky as illustrated below. (6) |
THREE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Inventory
Control |
|
Priority
Planning |
|
Capacity
Requirements
Planning |
- • Order the right part.
- • Order the right quantity.
- • Order at the right time.
|
|
- • Order with the right due date.
- • Keep the due date valid.
|
|
- • Plan for a complete load.
- • Plan an accurate (valid) load.
- • Plan for an adequate time span to view future loads.
|
|
|
|
|
3. ADVANTAGES OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
THE MRP SYSTEM |
At present, many small and medium-sized manufacturing companies use an MRP System or plan to install one in the near future. The MRP system generally handles a large variety of products, parts, components, and raw materials. In addition, this system may offer several advantages outlined below. |
ADVANTAGES OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
1. |
Reduction of the average level of inventory. |
2. |
Ability to keep track of material requirements. |
3. |
Ability to evaluate the capacity requirements generated by the master schedule. |
4. |
Improved availability of raw materials, components, and parts. |
5. |
Improved utilization of operational capacity and manpower resources. |
6. |
Reduction in idle time in the facility. |
7. |
Reduction in machine set-up and tear-down costs. |
8. |
Improved flexibility of master production schedule. |
9. |
Improved production flow. |
10. |
Improved allocation of production times. |
11. |
Reduction in overall manufacturing costs. |
12. |
More reliable delivery dates to customers. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL BENEFITS PROVIDED BY THE MRP SYSTEMS |
The MRP System can also inform the production manager in advance if required delivery dates are achievable. Furthermore, it changes due dates for orders and facilitates capacity requirements planning.
Many companies, that have used the MRP system, have reported a substantial reduction in inventory investment costs and an overall improvement in productivity and cost-efficiency. |
|
|
4. THREE SOURCES OF INFORMATION FOR THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
APPLICATION OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
In order to use the MRP System it is necessary to collate information from three sources illustrated below. |
THREE SOURCES OF INFORMATION FOR THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
The Master
Production
Schedule (MPS) |
|
The Bill
Of Materials
File (BOM) |
|
The Inventory
Status
File |
This schedule is prepared on the basis of actual customers' orders and predicted demand. The MPS indicates the quantity and date of each production order. |
|
This file contains details of all raw materials, parts, components, sub-assemblies, and assemblies required to complete a product. |
|
This file contains detailed information about the quantity of each item available on hand, on order, and committed for use in the manufacturing process. |
|
|
The MRP system is designed to run on a regular basis, say once a week, and must be supported by accurate and updated information drawn from all the aforementioned sources. This system is schematically presented below. |
THREE SOURCES OF INFORMATION FOR THE MRP SYSTEM |
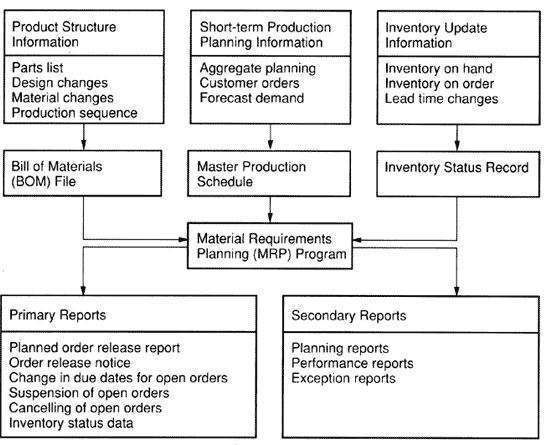
|
|
|
5. MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE |
 |
|
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE |
A Master Production Schedule (MPS), or Master Schedule, is the prime input element for the MRP system.
This schedule is generally developed on a regular basis and contains all confirmed Customer Orders and Additional Inventory Requirements. The customer orders include the quantities and delivery dates of required products while additional inventories are determined in accordance with forecast for product demands.
The types and quantities of products may vary from one week to another depending upon immediate customer needs and short-term forecast demands. Master production schedules, therefore, should be examined for availability of materials, operational capacity, and labor, and then revised and developed again. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
6. HOW DOES THE MRP SYSTEM WORK? |
 |
|
ILLUSTRATION OF A MATERIAL REQUIREMENTS PLANNING SYSTEM |
Consider, for example, a Master Production Schedule For ABC Manufacturing Company which makes filing cabinets and office furniture. A portion of such a schedule is presented below.
This example is followed by an illustration of a Bill Of Materials and a Product Structure Tree, which will provide important information related to the number of parts and components in each part which must be scheduled for production planning purposes.
All illustrations related to MRP System and presented below have been produced by James B. Dilworth, a well-known author and Professor of Operations Management.
It is essential that you and your operations management team become familiar with all elements of the MRP System. Only then will you be able to appreciate the scope of benefits offered by this system, and its ability to secure your company's successful performance in a highly competitive manufacturing environment. |
|
|
7. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE |
 |
|
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE |
Item |
Week No. |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
001 3-drawer file |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
100 |
|
100 |
005 4-drawer file |
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
60 |
120 |
|
60 |
|
100 |
007 desk |
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
150 |
100 |
|
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, p. 289. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
8. BILL OF MATERIALS FILE |
 |
|
BILL OF MATERIALS FILE |
The Bill Of Materials (BOM) File contains detailed information about the quantity of materials and components which must be pre-purchased or manufactured in order to complete a specified number of finished products. This file includes a detailed breakdown, or "explosion" of all components for every product manufactured by the company and provides the second input for the MRP system.
Each Bill of Materials contains a comprehensive parts list which summarizes the exact quantities of all components, sub-assemblies, and assemblies required to complete a particular product.
In addition, a Bill of Materials provides information pertaining to the manufacturing methods of each component as summarized in the appropriate Route Sheet. All product design modifications and changes in material and production sequence are also included in this file.
Since the final assembly might consist of several sub-assemblies, the end-product may be presented as a Multi-Level Component Structure, or a Product Structure Tree.
The Bill Of Materials and Product Structure Tree for the filing cabinet produced by ABC Manufacturing Company are presented below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
9. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
BILL OF MATERIALS |
 |
|
BILL OF MATERIALS |
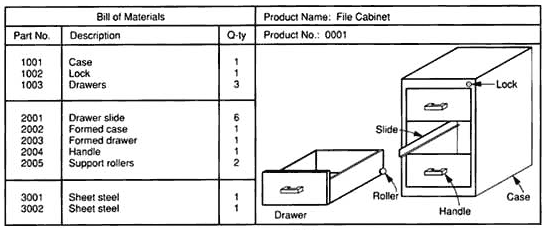
|
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, pp. 292 - 293. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
10. PRODUCT STRUCTURE TREE |
 |
|
PRODUCT STRUCTURE TREE |
The Product Structure Tree for the filing cabinet contains four levels of products, components, and materials.
Each "lower level" represents the "component level" for the one above it. Level 3, for example, contains materials which are needed for manufacturing components presented in Level 2. Components in Level 2, in turn, are required for completing "parent sub-assemblies" in Level 1. Finally, "parent sub-assemblies" and components in Level 1 are used in the assembly of the finished product in Level 0.
Each item specified in the Product Structure Tree is identified by several elements, as illustrated below. |
ELEMENTS OF THE PRODUCT STRUCTURE TREE |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Part
Number |
|
Quantity
Per One Assembly |
|
Lead
Time |
|
|
WHAT IS LEAD TIME? |
Lead Time is the estimated number of weeks, which have to be allowed for obtaining specific materials and parts, manufacturing and sub-assembling components, and assembling the final product. |
The Product Structure Tree for the filing cabinet produced by ABC Manufacturing Company is presented below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
11. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
PRODUCT STRUCTURE TREE |
 |
|
BILL OF MATERIALS |
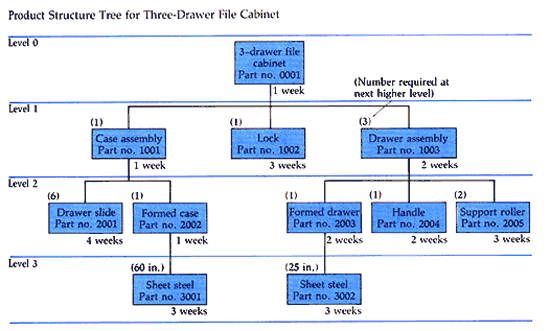
|
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, pp. 292 - 293 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
12. INVENTORY STATUS FILE |
 |
|
INVENTORY STATUS FILE |
The Inventory Status File represents the third major input for the MRP system. This file contains a detailed and updated record regarding the status of every inventory item, i.e., raw materials, components, sub-assemblies, and assemblies.
Some items required for a particular job could be available in the stores, but others should be purchased to meet specific material requirements. Inventory items are usually grouped into categories and coded by an individual identification number for easy reference.
The details regarding each item are summarized in an Inventory Status Record and include important information, as illustrated below. The Inventory Status Record, or Inventory Record, may contain additional information pertaining to subsidiary data such as order details, pending action, or order changes.
All information pertaining to inventory status is updated on a regular basis to ensure effective material requirements planning. A typical Inventory Record of the drawer assembly for the file cabinets produced by ABC Manufacturing Company is presented below. |
INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THE INVENTORY STATUS RECORD |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Item Number
Or Item Code, Description, Name, And
Lead Time |
Gross Requirements Of
Inventory |
Scheduled Receipt
Of
Inventory
(Open Orders) |
Expected Quantity
Of
Inventory
On Hand |
Planned
Order
Releases |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
13. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
INVENTORY RECORD |
 |
|
INVENTORY RECORD |
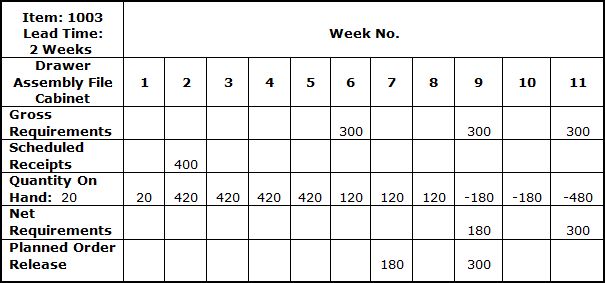 |
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, p. 295. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
14. WHAT CAN THE MRP SYSTEM DO FOR YOUR COMPANY? |
 |
|
MAIN ELEMENTS OF THE MRP SYSTEM |
The MRP System uses the Master Production Schedule, the Bill Of Materials File, and the Inventory Status File to determine specific manufacturing requirements at any given moment as illustrated below. |
SPECIFIC MANUFACTURING REQUIREMENTS
DETERMINED BY THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Net Requirements
For Materials |
|
Net Requirements
For Components |
|
Net Requirements
For Sub-Assemblies |
|
|
Additional information determined by the MRP system is contained in three reports outlined below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PROVIDED BY THE MRP SYSTEM |
1. |
The Master Production Schedule.
The Master Production Schedule specifies the type, quantity, and completion date of a particular product. |
2. |
The Bill Of Materials File.
The Bill Of Materials File provides information about the type, quantity, and lead time of all materials and components required for any finished product. |
3. |
The Inventory Status File.
The Inventory Status File summarizes the quantities on hand and scheduled receipts per component (i.e., previously released orders). |
|
Upon processing the aforementioned information, the MRP system will provide two options outlined below. |
TWO OPTIONS PROVIDED BY THE MRP SYSTEM |
1. |
The inventory on hand plus previously released orders is sufficient to meet scheduled manufacturing requirements. Hence, there is no need to release additional purchase or production orders. |
2. |
The inventory on hand plus previously released orders is not sufficient to meet scheduled manufacturing requirements. In this instance, additional purchase or manufacturing orders should be released in accordance with the net requirements and lead time for a particular component. |
|
|
|
15. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
CALCULATION OF NET REQUIREMENTS |
 |
|
CALCULATION OF NET REQUIREMENTS |
Consider, for example, the Inventory Status Record for the drawer assembly presented earlier. According to this example, the Net Requirements for the item in Period 9 can be determined as follows:
( +) Gross Requirements: + 300
( - ) Scheduled Receipts: - 0
( - ) On Hand: - 120
( =) Net Requirements: + 180
Since the Lead Time for the drawer assembly is two weeks, the Net Requirements must be scheduled two weeks ahead. Thus, the Planned Order Release of 180 is entered in Period 7 to meet the above manufacturing requirements. |
|
|
16. CONTINUOUS FEEDING OF INFORMATION INTO THE MRP SYSTEM |
 |
|
FEEDING INFORMATION INTO THE MRP SYSTEM |
All information must be fed into the MRP System continuously and accurately to ensure effective production performance. The MRP system, in turn, will process such information and determine Net Requirements and Order Release Dates for every material and component required for current manufacturing needs.
The action of the MRP system cuts across all levels of the Product Structure Tree and converts Gross Requirements of the Master Production Schedule into Net Requirements for individual components. The conversion of such requirements is illustrated below. |
|
|
17. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
MRP SYSTEM LINKAGE BETWEEN FILES |
 |
|
MRP SYSTEM LINKAGE BETWEEN FILES |
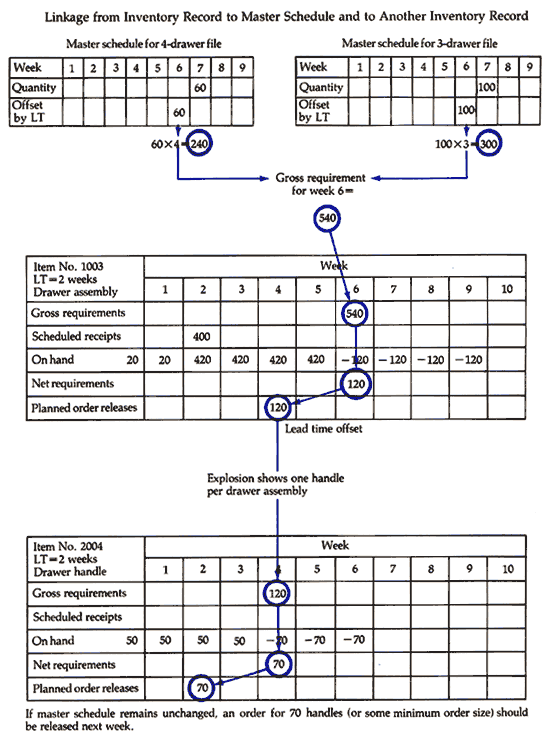
|
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, p. 298. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
18. TIME-SCALED ASSEMBLY CHART |
 |
|
TIME-SCALED ASSEMBLY CHART |
Once all Net Requirements of individual components are identified, a Time-Scaled Assembly Chart needs to be prepared. The prime purpose of this chart is to illustrate when orders for various materials and components should be released to ensure timely assembly of the finished product.
A typical Time-Scaled Assembly Chart for the three-drawer file cabinet is presented below. |
|
|
19. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
TIME-SCALED ASSEMBLY CHART |
 |
|
TIME-SCALED ASSEMBLY CHART |
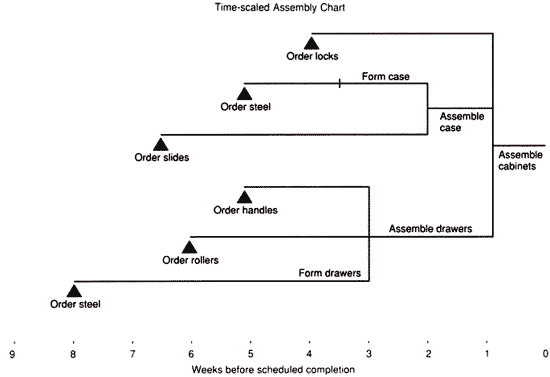
|
© James B. Dilworth, Production and Operations Management, 3rd ed., 1986, p. 299. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., Reprinted with permission. |
|
|
20. THE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY REPORTS |
 |
|
MRP SYSTEM REPORTS |
As a result of extensive computations, the MRP System produces a number of important documents. These documents are generally classified into two types outlined below. (7) |
PRIMARY REPORTS |
1. |
Planned Orders.
Planned orders, or a schedule indicating the amount and timing of future orders. |
2. |
Order Releases.
Order releases, authorizing the execution of planned orders. |
3. |
Changes.
Changes in due dates of open orders due to rescheduling. |
4. |
Cancellations Or Suspensions.
Cancellations or suspensions of open orders due to cancellation or suspension of orders on the Master Production Schedule. |
5. |
Inventory Status Data.
Inventory Status Data provides information about various types of inventory. |
|
SECONDARY REPORTS |
1. |
Planning Reports.
Planning reports are used, for example, in forecasting inventory and specifying requirements over some future time horizon. |
2. |
Performance Reports.
Performance reports are used for purposes of pointing out inactive items and determining the agreement between actual and programmed item lead times and between actual and programmed quantity usages and costs. |
3. |
Exceptions Reports.
Exceptions reports point out serious discrepancies, such as errors, out-of-range situations, late or overdue orders, excessive scrap, or non-existent parts. |
|
|
|
21. WHAT IS MRP II? |
 |
|
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEM (MRP II) |
The MRP System is widely used in various manufacturing industries and has often proved successful. This system has been modified to incorporate additional functional parameters. Such a system is known as Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II).
The main purpose of the MRP II is to plan, monitor, and integrate various resources and functions of a manufacturing company including operations, purchasing, accounting, and marketing.
The MRP II was not developed as a replacement of the MRP system. Instead, it was designed to enhance the value of the MRP system by integrating main operational planning activities on a company-wide basis. |
| A simplified overview of the MRP II System is presented below. |
| |
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEM (MRP II) |
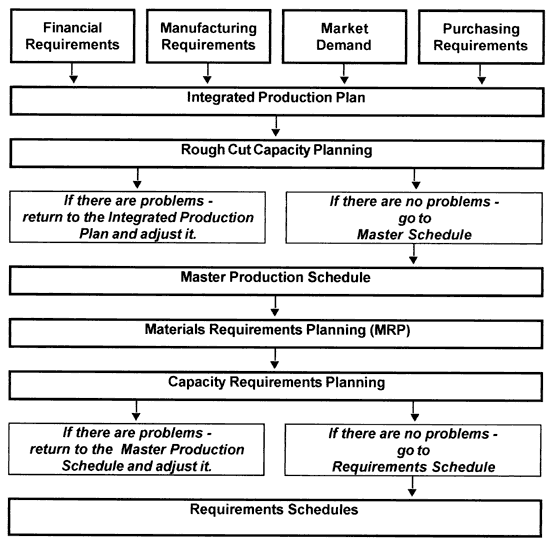
|
ADDITIONAL BENEFITS OF THE MRP II SYSTEM |
In addition, most MRP II Systems have the capacity to provide operations managers with a simulated approach and help finding answers to "what if" questions. This enables managers to enter data into the computer and run simulation tests with an objective to identify a broad range of consequences in production output by changing production input variables. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
22. WHAT IS ERP? |
 |
|
ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING (ERP) |
The most recent development in the area of manufacturing resource planning is called Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
ERP represents an improved version of the MRPII and it is designed to cover a broad range of functions within a manufacturing company. The ERP System deals with materials planning, efficient production, profitability, customer’ satisfaction - almost every aspect of business.
This system also incorporates the principles of global supply chain management, in which the value of every activity in the supply chain is analyzed, along with the growing development of Internet or web-enabled procurement systems. |
BASIC COMPONENTS OF ERP |
|
| |
WHAT IS INSIDE THE ERP SYSTEM? |
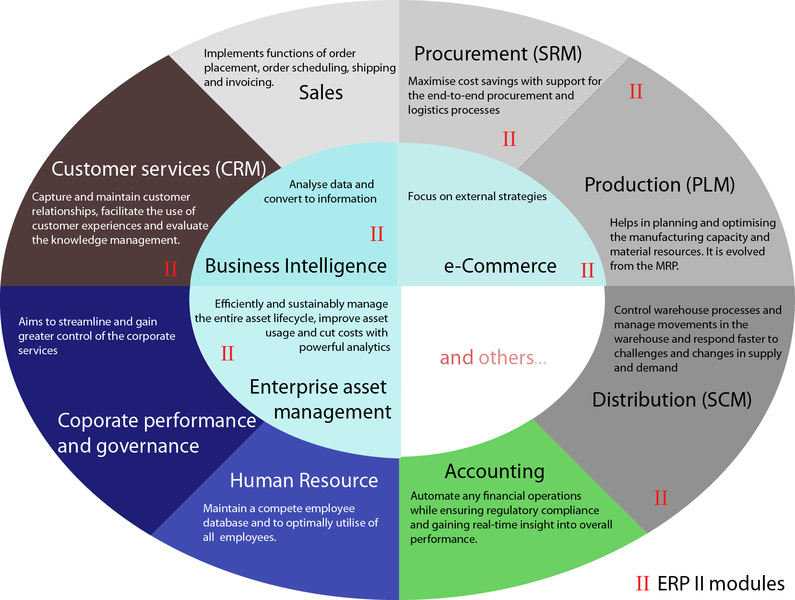
|
Source: Wikimedia Commons, File ERP II, Author Shing Hin Yeung, 2013.
|
ADVANTAGES OF ERP |
1. |
Improved inventory management with lower stock level requirements. |
2. |
Improved customer service and better delivery results. |
3. |
More accurate costing of products. |
4. |
Improved productivity and better utilization of sub-contractors. |
5. |
Faster response to changing schedules and requirements. |
6. |
Improved quality of products. |
7. |
Improved integration of various operational activities within the company. |
8. |
Overall cost-effective performance and relatively fast return on investment. |
|
| |
DISADVANTAGES OF ERP |
Probably the main disadvantage of any ERP System is its high initial cost. The basic modules of a typical ERP System may cost several hundreds of thousands of dollars and the cost of a fully integrated ERP System package may even reach a million dollars. Moreover, the ERP implementation into the company’s infra-structure may require additional investment and could subsequently be prohibitively expensive for many business owners of small and medium-sized companies.
The ERP System may cause reduced flexibility in planning and control of operational activities by becoming a dominant element in the operations department and by providing less freedom and creativity for employees. The ERP System may also cause a certain degree of discomfort for some employees within the organization during the initial implementation stages. However, once the ERP System is fully tested and implemented, it is expected to be well-accepted by management and employees alike, and play a positive role in the overall long-term success of the organization. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
23. LATEST MRP AND ERP DEVELOPMENTS |
 |
|
DEVELOPMENTS IN THE AREA OF
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING |
The ultimate success of manufacturing companies in the current highly competitive business environment depends upon their cost-efficiency and the ability to adapt to the constantly changing conditions in the marketplace. Management must be able to meet their customers’ demands for higher quality products and services, lower prices and faster deliveries.
To compete effectively in global markets, manufacturing companies of all sizes must consider utilizing new Manufacturing Resource Planning and Decision Support Systems within their organization. There are a number of new software programs related to manufacturing resource planning systems available in the marketplace at present, such as MRPII and ERP, discussed earlier.
One of the leading MRP products is Caliach MRP, offered by Manufacturing And Computer Systems. Caliach MRP is used by over 70,000 users and its average price is about $20,000, according to the survey conducted by the Association For Operations Management, formerly known as The American Production And Inventory Control Society (APICS).
One of the leading providers of ERP Systems is SAP AG which has over 89,000 clients worldwide. Other programs are designed to facilitate efficient planning and control within a manufacturing company by providing an extensive database through a network of computer terminals.
Business owners and operations managers are strongly advised to investigate the advantages and disadvantages of various MRP, MRPII and ERP software packages specifically developed to improve the cost-efficiency and productivity of manufacturing companies, and select the most suitable program, based on their specific long-term requirements. |
MRP, MRPII, AND ERP SOFTWARE PROGRAMS |
There are several Manufacturing Resource Planning Software Systems and Enterprise Resource Planning available for small and medium-sized businesses. Some of the some of the most popular MRP - MRPII - ERP programs are presented below. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
You can obtain additional information about MRP, MRP II and ERP Systems online from the following sources:
|
|
|
24. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
25. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
Ultimately, The MRP System Means: Maximizing Revenues And Profits!
|
Go To The Next Open Check Point In This Promotion Program Online. |
| |
|










